Electrical & Instrumentation
- Home
- Electrical & Instrumentation
Electrical
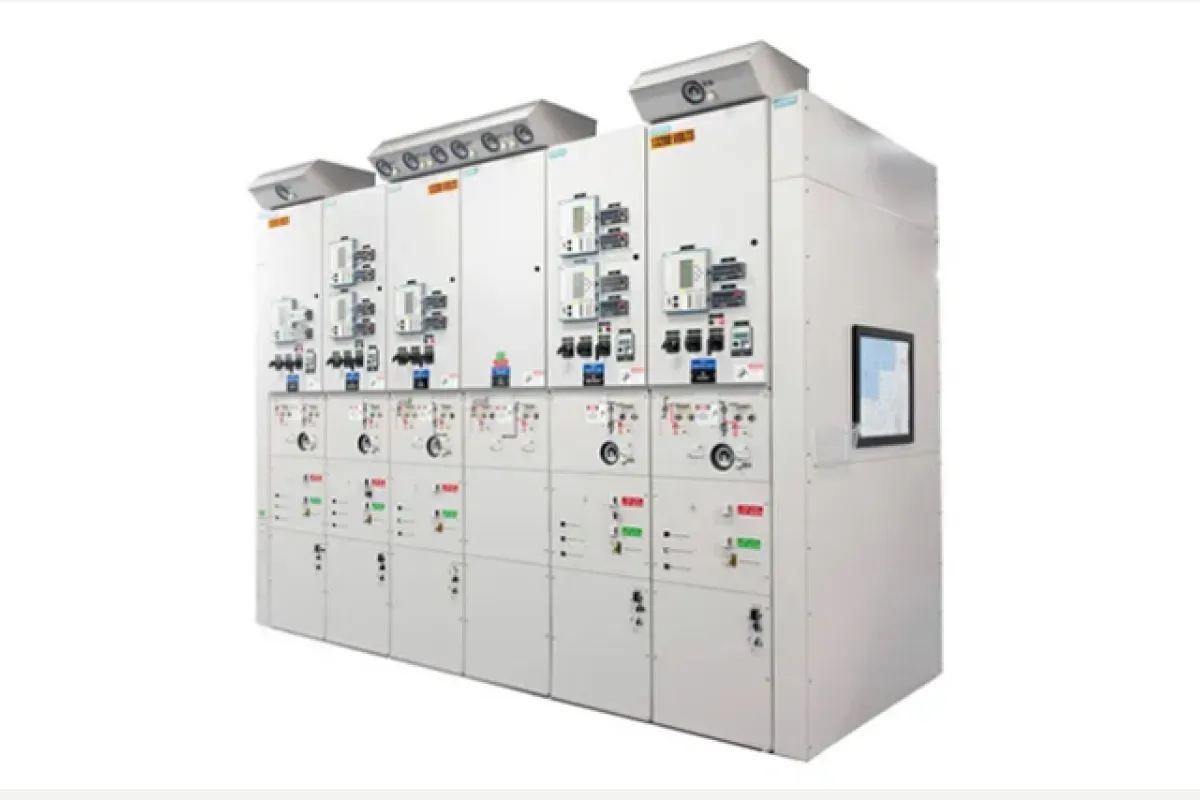

Switchgear
Function
Safeguards electrical systems by managing, protecting, and isolating equipment.
Examples
⮞ Circuit Breakers: Automatically interrupt excessive currents to prevent damage. ⮞ Disconnect Switches: Ensure safe disconnection for maintenance. ⮞ Fuses: Provide rapid response to overcurrent by breaking the circuit.
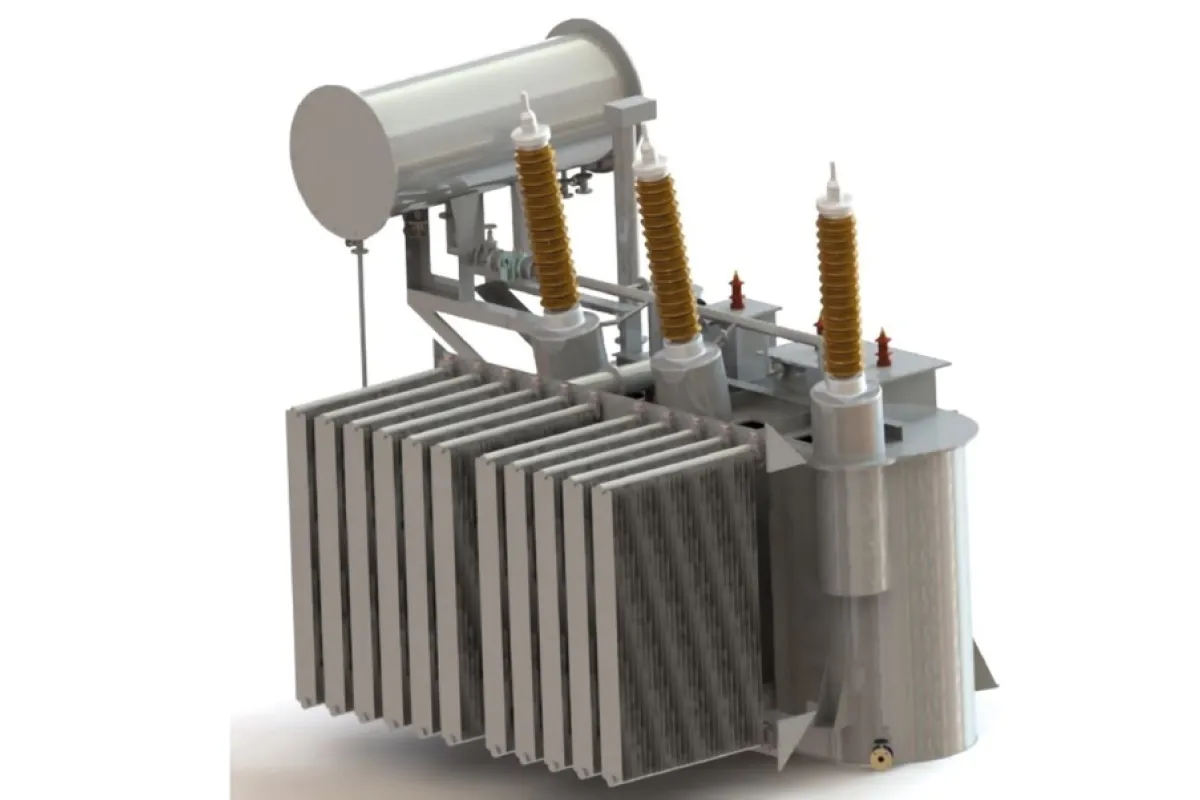
Transformers
Function
Regulates voltage levels in power systems by stepping them up or down as needed.
Examples
⮞ Power Transformers: Handle high-voltage transmission for efficient energy transfer. ⮞ Distribution Transformers: Deliver usable voltage to end-users. ⮞ Instrument Transformers: Measure and monitor electrical parameters (current and potential).
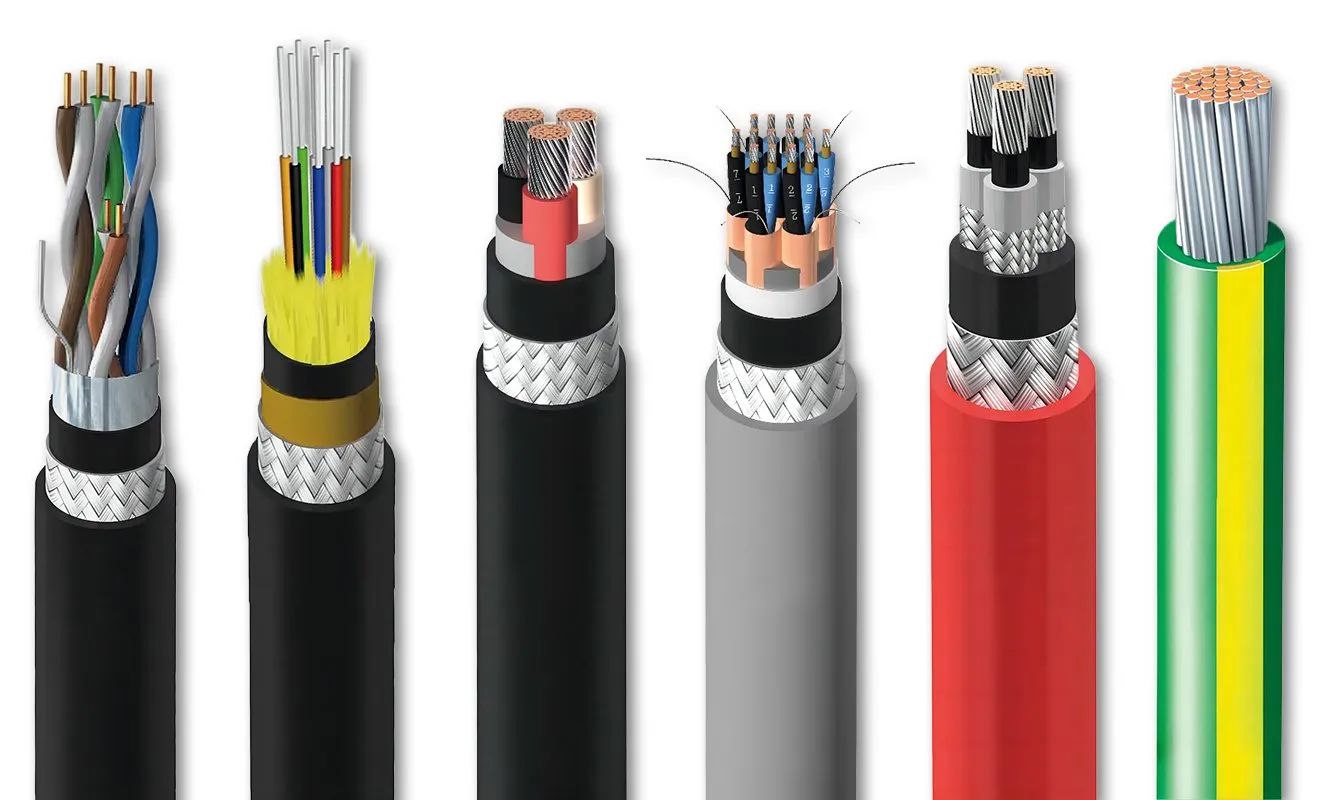
Cables
Function
Transmit electrical power between components in a system.
Examples
⮞ Copper Cables: Common for general electrical applications. ⮞ Aluminum Cables: Lighter and more cost-effective for some applications. ⮞ Fiber Optic Cables: Transmit data using light signals. ⮞ FControl Cables: Used for low-voltage control signals. ⮞ Instrumentation Cables:Designed for precise measurement and control signals.
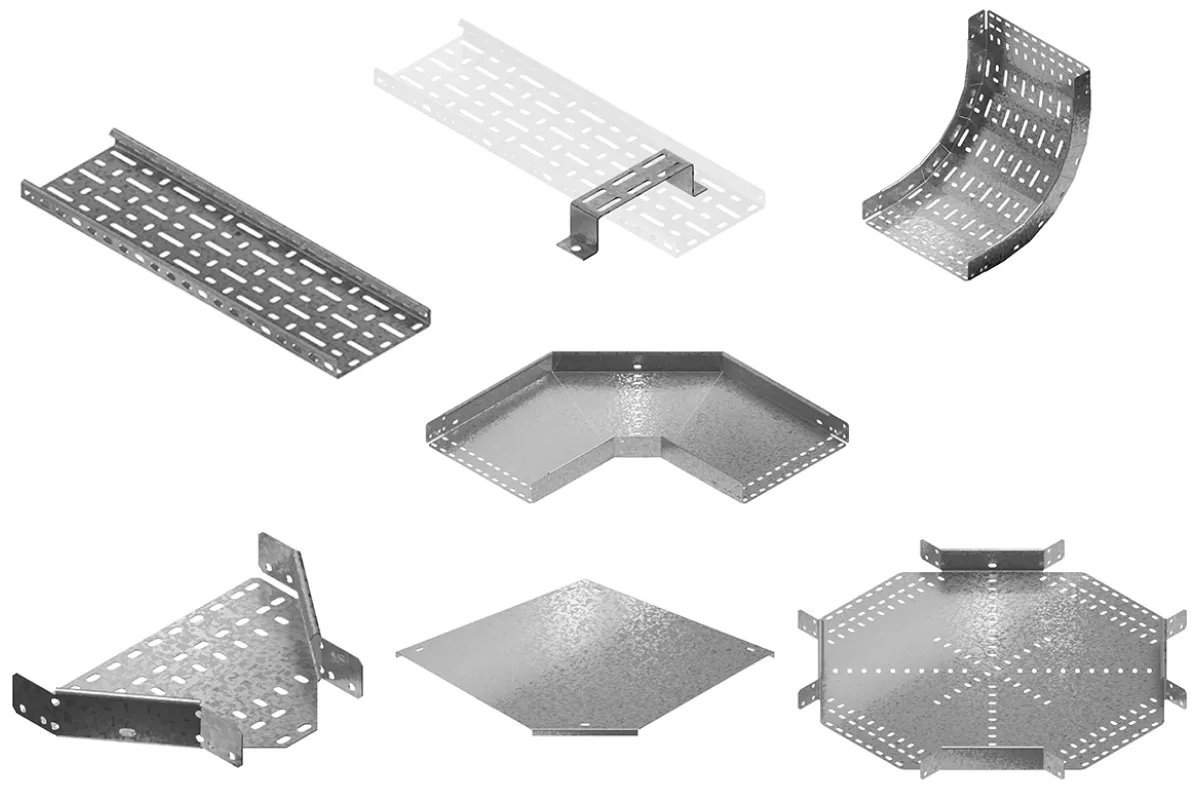
Cable Trays
Function
Support and protect electrical cables, wires, and conduits within a structured system.
Examples
⮞ Ladder Trays: Open sides for easy cable installation and inspection. ⮞ Trough Trays: Enclosed sides for better protection and cable management. ⮞ Wire Mesh Trays: Allow for good ventilation and heat dissipation. ⮞ Perforated Trays: Improve airflow and reduce weight. ⮞Cable Ladders: Simple and versatile for various cable sizes and configurations.
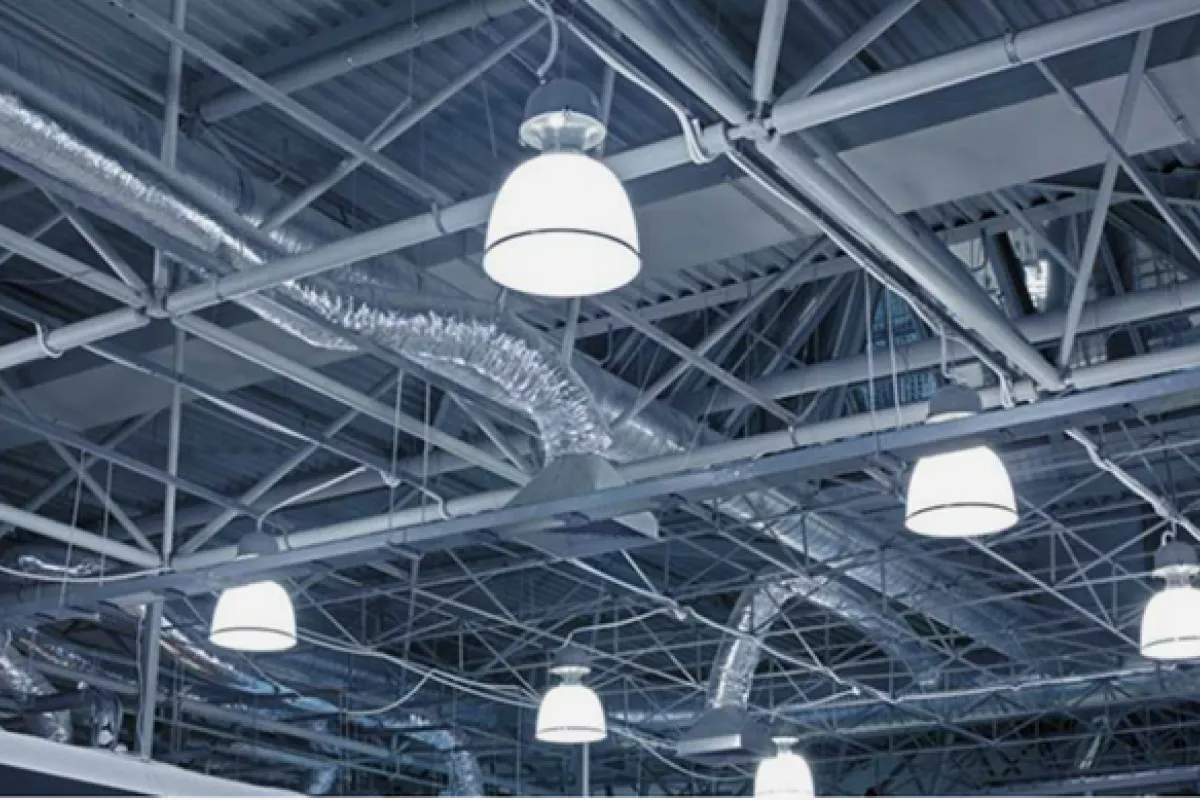

Lighting Systems
Function
Provide efficient and reliable illumination for facilities.
Examples
⮞ LED Lights: Energy-saving solutions for general lighting needs. ⮞ Explosion-Proof Lighting: Designed for safe use in hazardous environments. ⮞ Lighting Control Panels: Enable centralized and customizable lighting management.
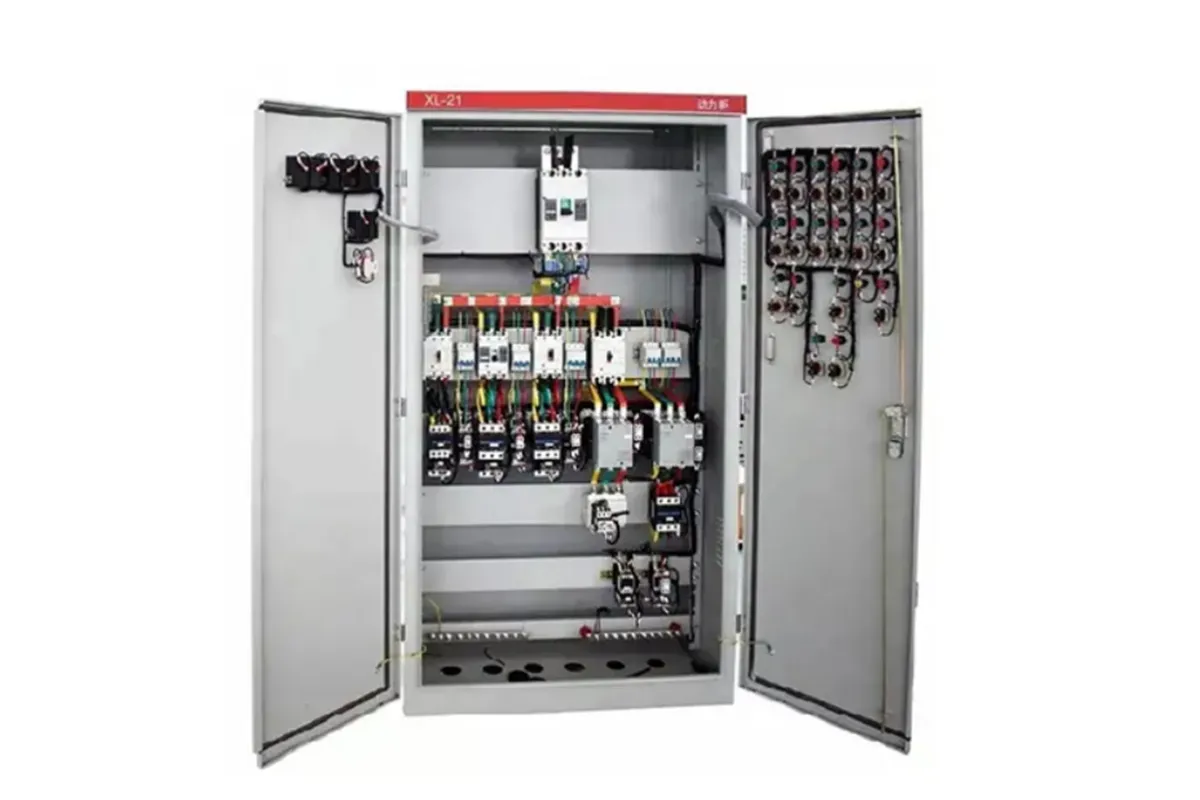

Power Distribution Panels
Function
Efficiently distribute electrical power throughout the facility.
Examples
⮞ Low Voltage (LV) Switchboards: Manage power distribution for residential and commercial setups. ⮞ Medium Voltage (MV) Switchboards: Handle higher voltage levels for industrial and large-scale applications.
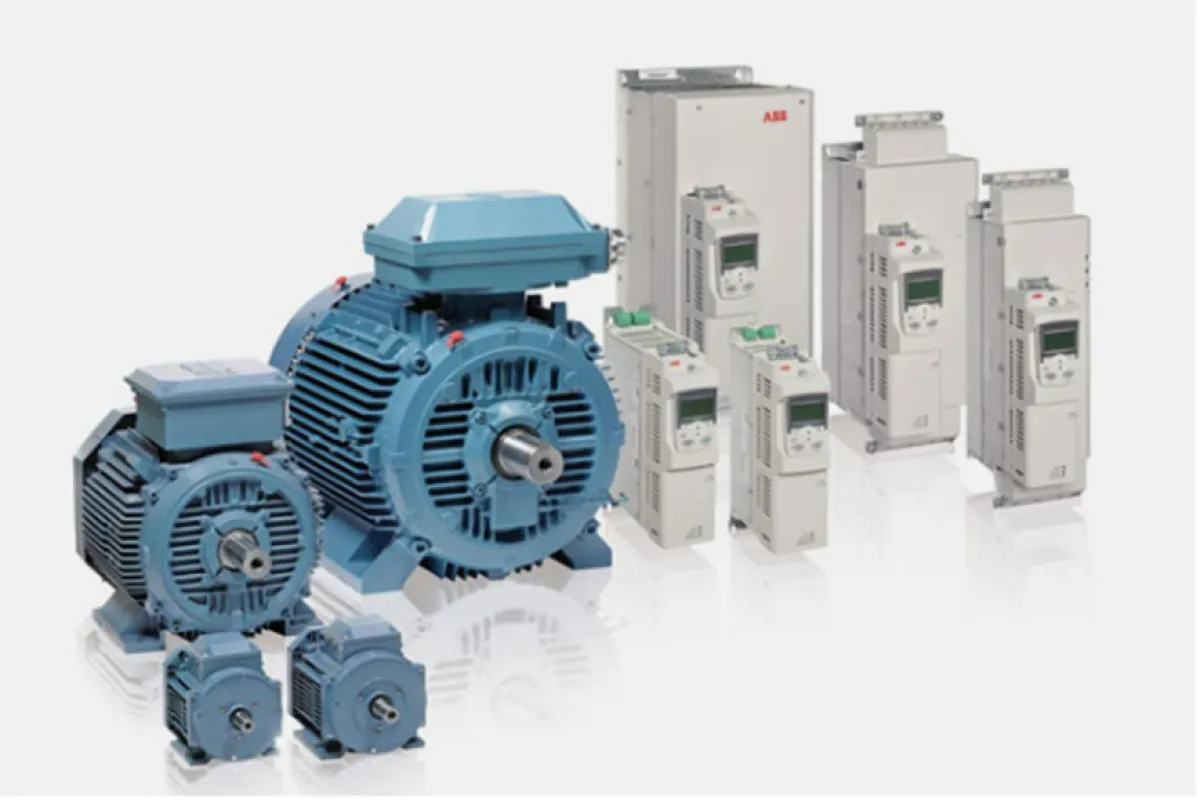

Motors and Drives
Function
Transform electrical energy into mechanical motion and control motor speed for optimal performance.
Examples
⮞ AC/DC Motors: Power diverse mechanical systems with precision. ⮞ Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Adjust motor speed and torque for energy-efficient operation.
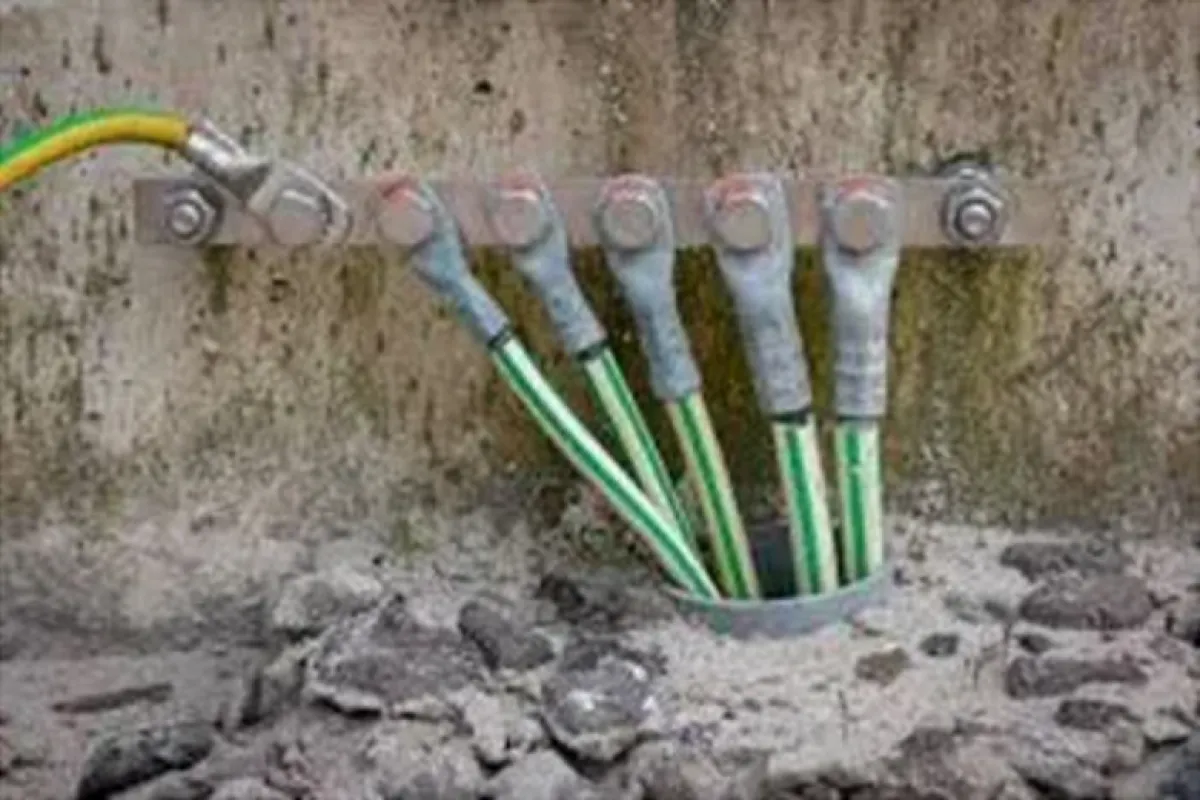

Earthing and Grounding Systems
Function
Safely dissipate fault currents to protect against electrical shocks and fire hazards.
Examples
⮞ Grounding Rods: Provide a direct path to the earth for fault current. ⮞ Earthing Mats: Ensure even fault current distribution in critical areas. ⮞Grounding Cables: Connect electrical systems securely to the grounding network.
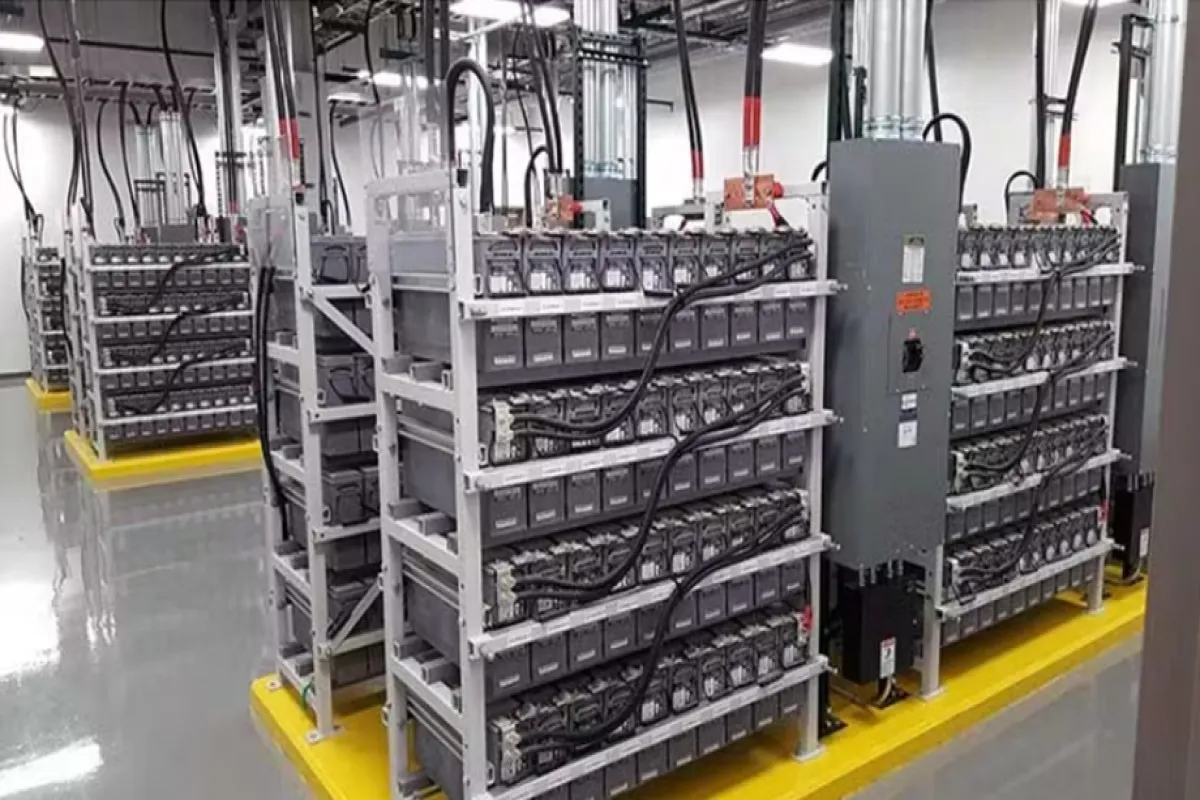

UPS and Battery Systems
Function
Ensure continuous power supply during outages to maintain critical operations.
Examples
⮞ Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Units: Deliver instant backup power for seamless transitions. ⮞ Battery Banks: Include lead-acid and lithium-ion options for reliable energy storage.
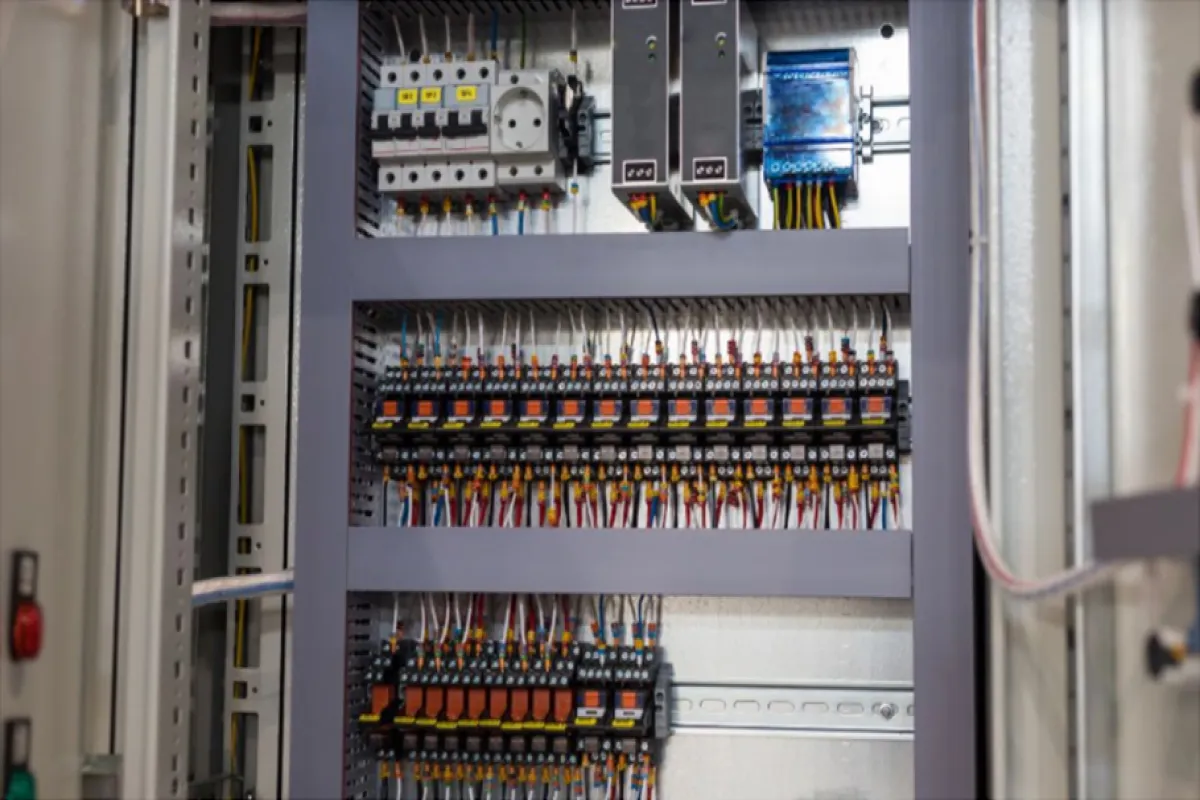

Control Panels
Function
Enclose and organize equipment for controlling machinery and industrial processes.
Examples
⮞ Motor Control Centers (MCCs): Centralize control of motors and related equipment. ⮞ Distribution Boards: Manage power distribution within a facility. ⮞ PLC Panels: Automate processes through programmable logic controllers.
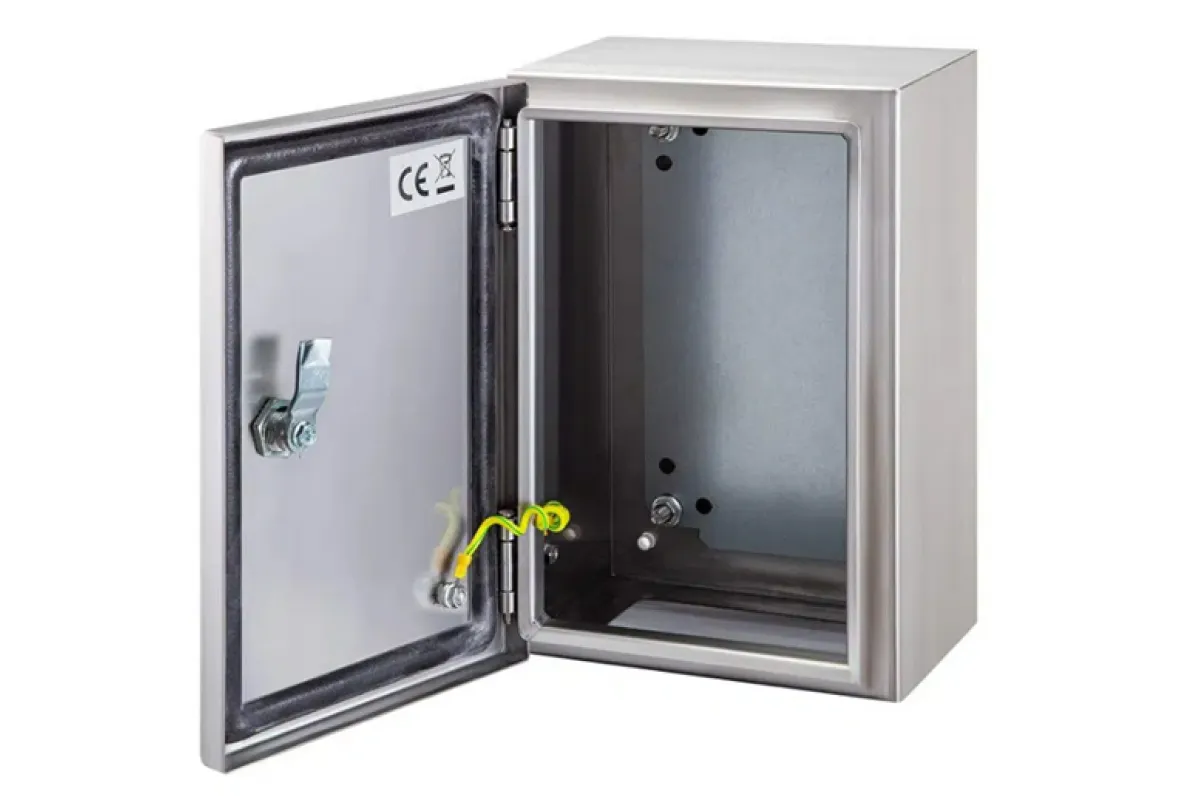

Electrical Enclosures
Function
Protect electrical equipment from environmental elements.
Examples
⮞ Junction Boxes: Safeguard electrical connections and wiring from dust, moisture, and physical damage. ⮞ Instrument Enclosures: Shield sensitive instruments from humidity, chemicals, and temperature extremes. ⮞Weatherproof Enclosures: Protect electrical equipment from rain, snow, and dust in outdoor environments. ⮞ Explosion-Proof Enclosures: Contain sparks or heat in hazardous environments to prevent explosions.
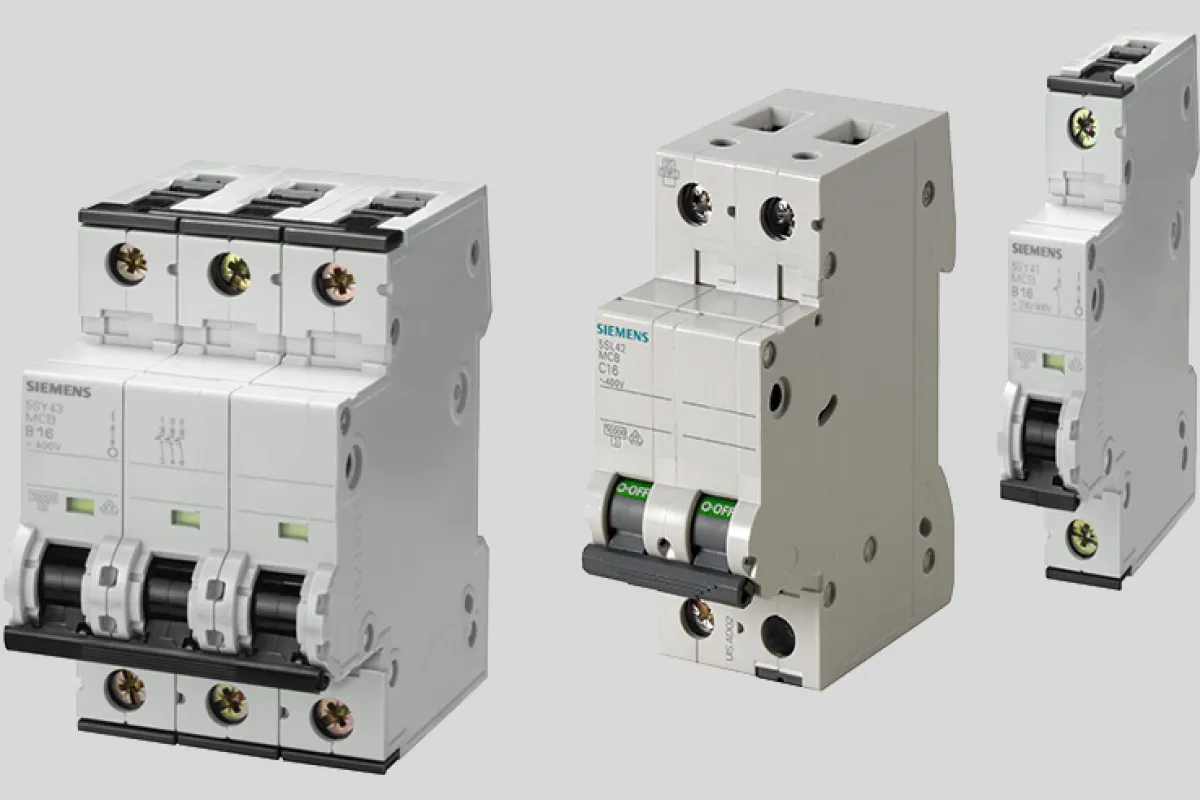

Circuit Breaker
Function
Automatically interrupts the flow of electric current in a circuit to protect electrical devices from damage caused by overloads or short circuits.
Examples
⮞ Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs): Commonly used in industrial and commercial applications. ⮞ Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs): Used in residential and light commercial applications. ⮞Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs): Used in high-voltage applications. ⮞ Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCBs): Used in high-voltage applications where space is limited.
Instrumentation
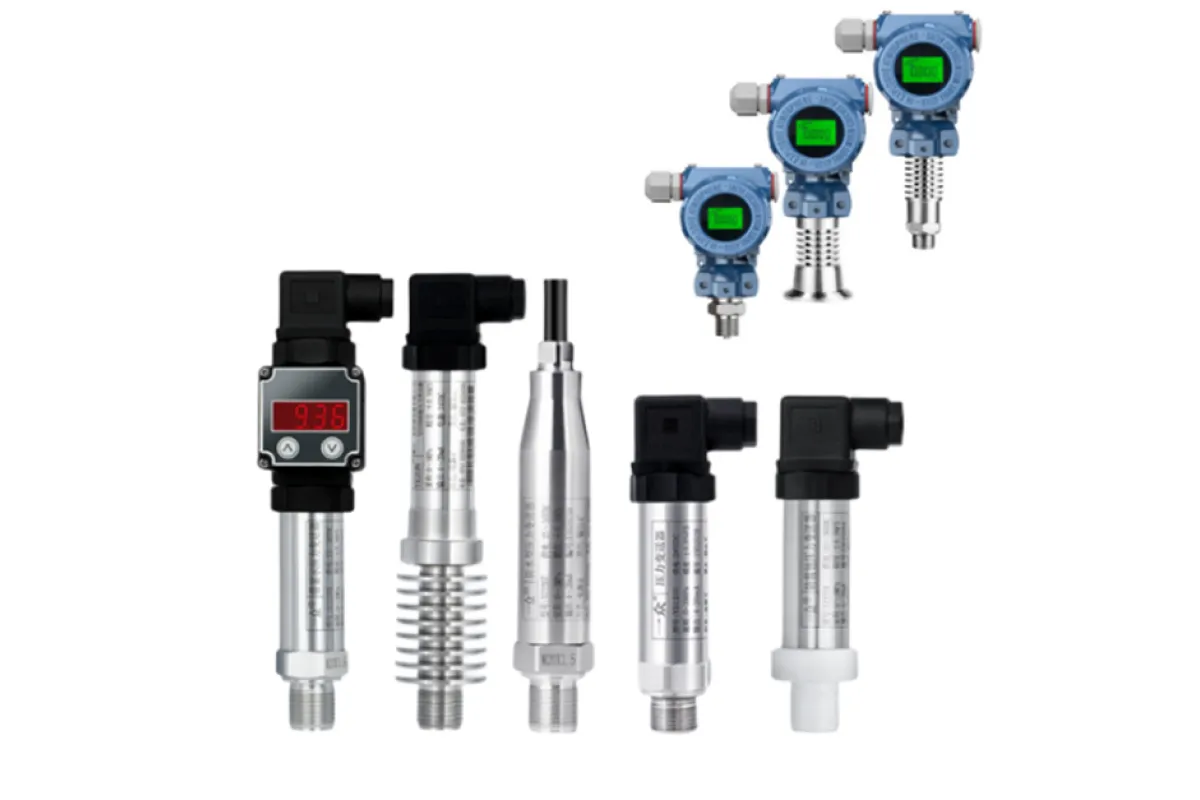

Sensors and Transmitters
Function
Detect and transmit data on process parameters.
Examples
⮞ Pressure Transmitters: Measure and transmit pressure readings within industrial systems. ⮞ Temperature Sensors (RTDs, Thermocouples): Detect temperature variations and provide data for process control. ⮞ Flow Transmitters (Ultrasonic, Magnetic): Measure and transmit flow rates of liquids or gases in pipes. ⮞ Level Sensors (Radar, Ultrasonic): Monitor and transmit the level of materials in tanks or vessels.
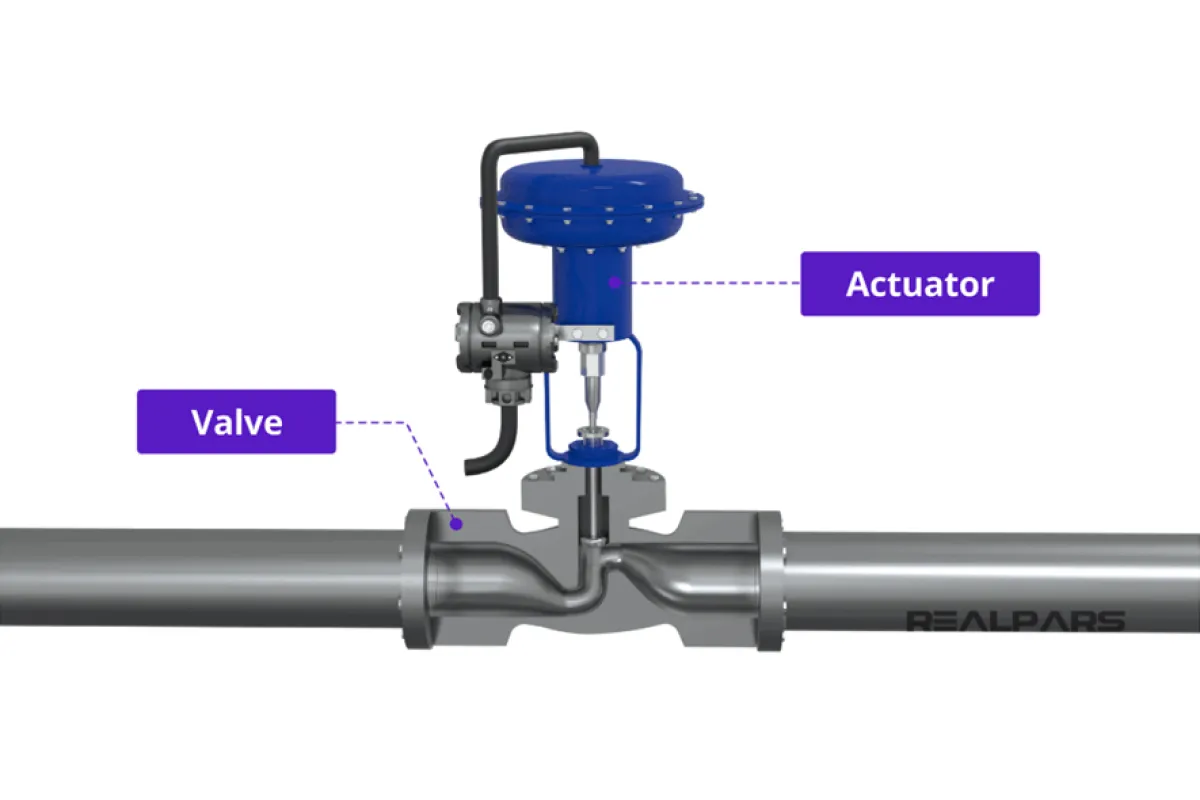
Control Valves and Actuators
Function
Regulate fluid or gas flow within a process.
Examples
⮞ Globe Valves: Control the flow of fluid by varying the size of the flow passage. ⮞ Ball Valves: Use a rotating ball to control the flow of fluid or gas. ⮞ Butterfly Valves: Control flow with a rotating disc to regulate or shut off the flow. ⮞ Electric Actuators: Operate valves automatically using electrical power for precise control. ⮞ Pneumatic Actuators: Use compressed air to operate valves, providing fast and efficient flow control.
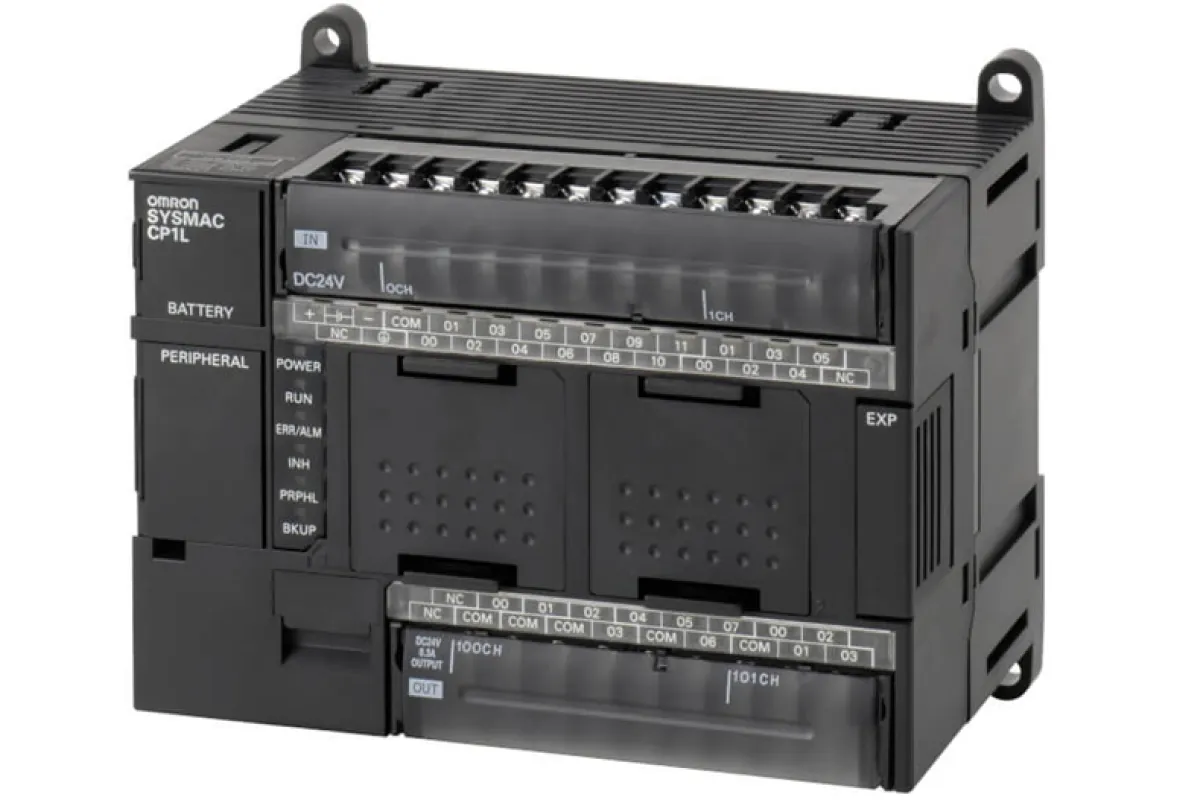

Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
Function
Automate control of industrial processes.
Examples
⮞ Allen-Bradley PLCs: Programmable logic controllers used for automating control systems in industrial applications. ⮞ Siemens S7 Series PLCs: A range of programmable logic controllers designed for efficient process automation and control.
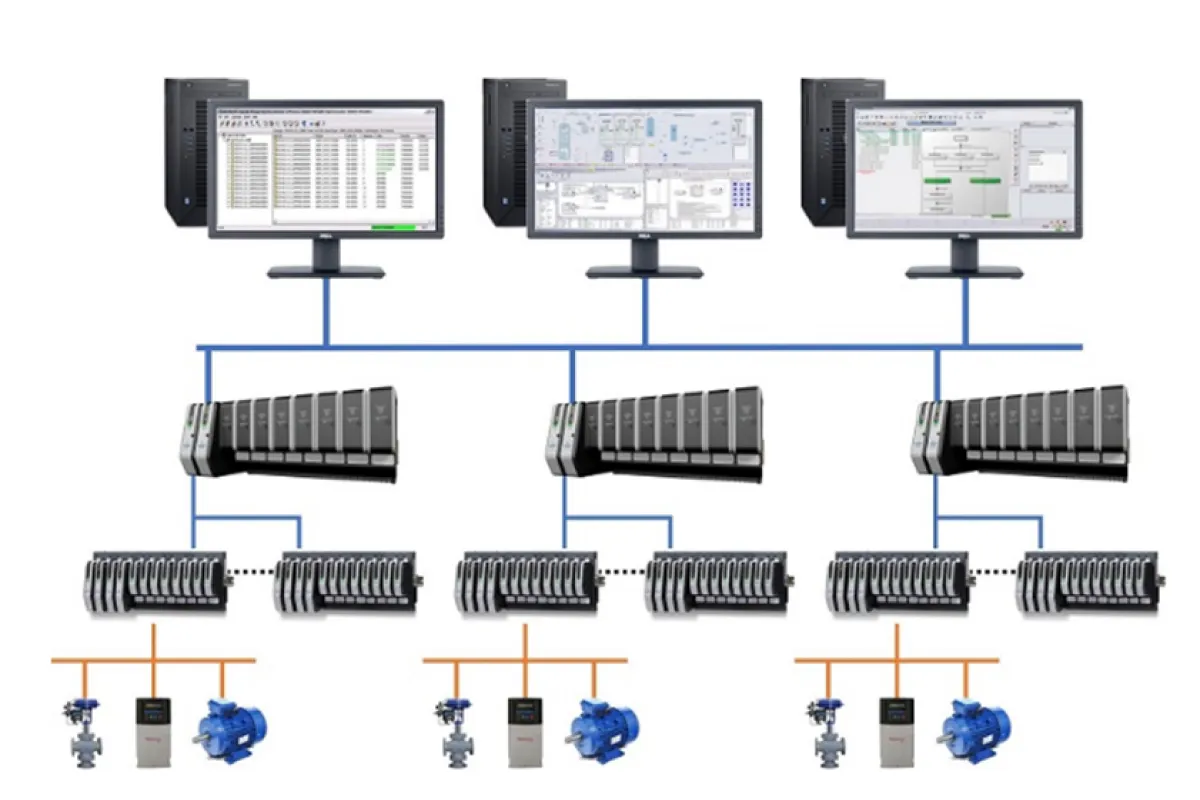
Distributed Control Systems (DCS)
Function
Centralize control for complex processes.
Examples
⮞ Honeywell Experion: A comprehensive control system that integrates process automation and optimization for industrial operations. ⮞ Emerson DeltaV: A process control system that centralizes control and monitoring for efficient management of complex processes.

Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs)
Function
Allow operators to interact with control systems.
Examples
⮞ Touchscreen Panels: Provide a user-friendly interface for operators to control and monitor systems. ⮞ Graphical Displays: Present visual representations of system data to help operators understand and manage control processes.
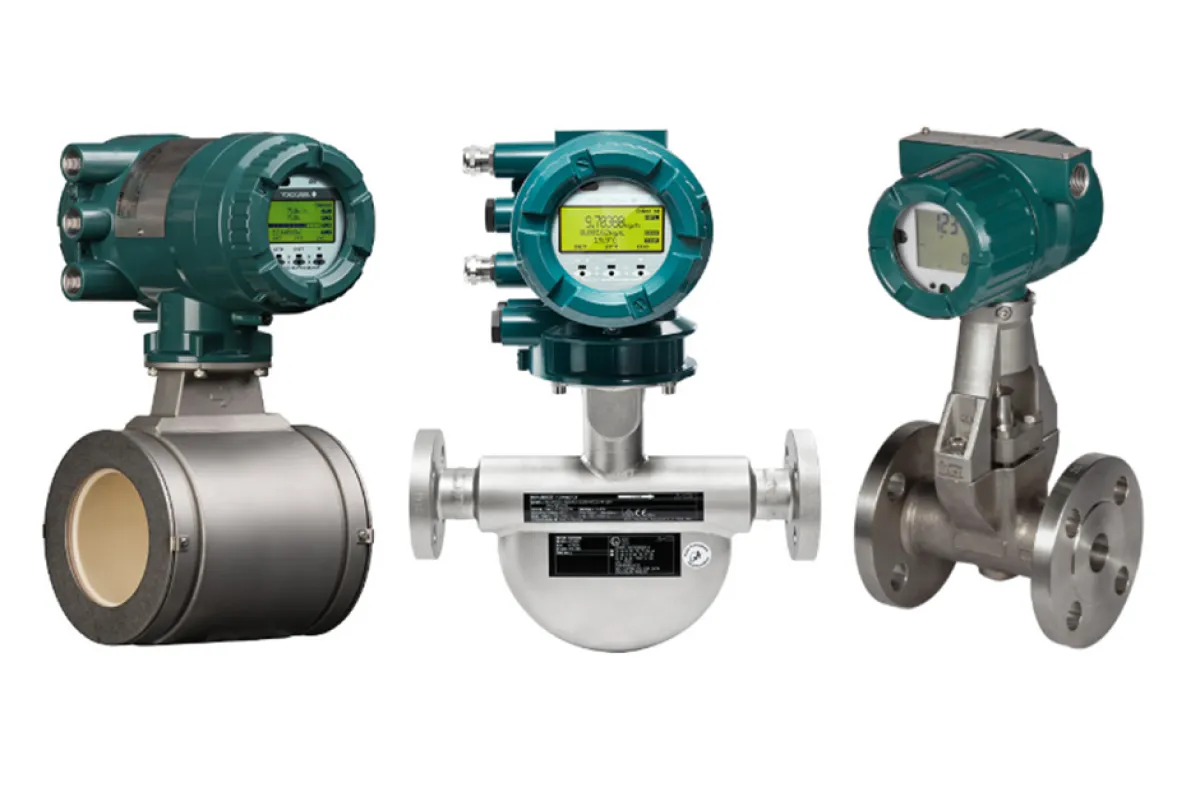

Flow Meters
Function
Measure the flow rate of liquids or gases.
Examples
⮞ Turbine Flow Meters: Measure flow by detecting the rotational speed of a turbine in the flow stream. ⮞ Coriolis Flow Meters: Measure mass flow by detecting changes in the vibration frequency of the flow tube. ⮞ Electromagnetic Flow Meters: Measure flow by detecting the voltage generated as a conductive fluid moves through a magnetic field.
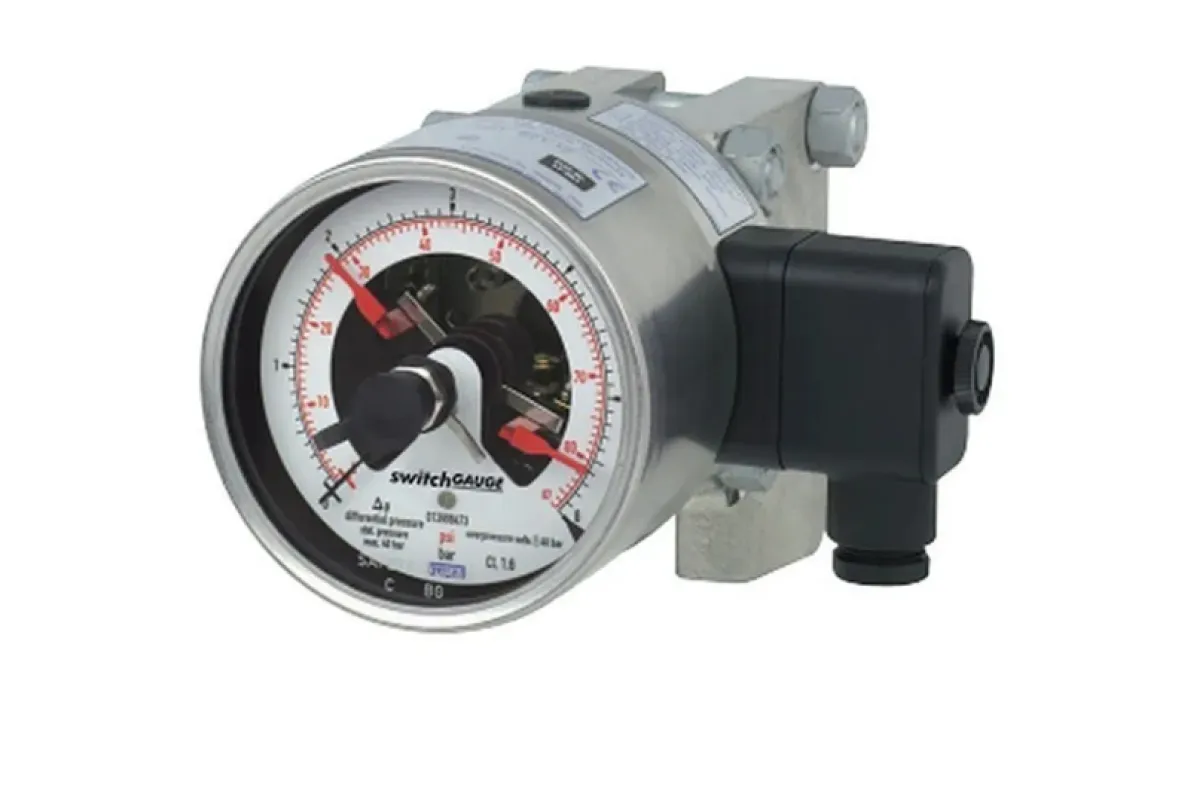

Pressure Gauges and Switches
Function
Monitor and measure system pressure.
Examples
⮞ Bourdon Tube Gauges: Measure pressure by detecting the deflection of a curved tube when exposed to pressure changes. ⮞ Diaphragm Switches: Monitor pressure by detecting the displacement of a diaphragm in response to pressure variations.
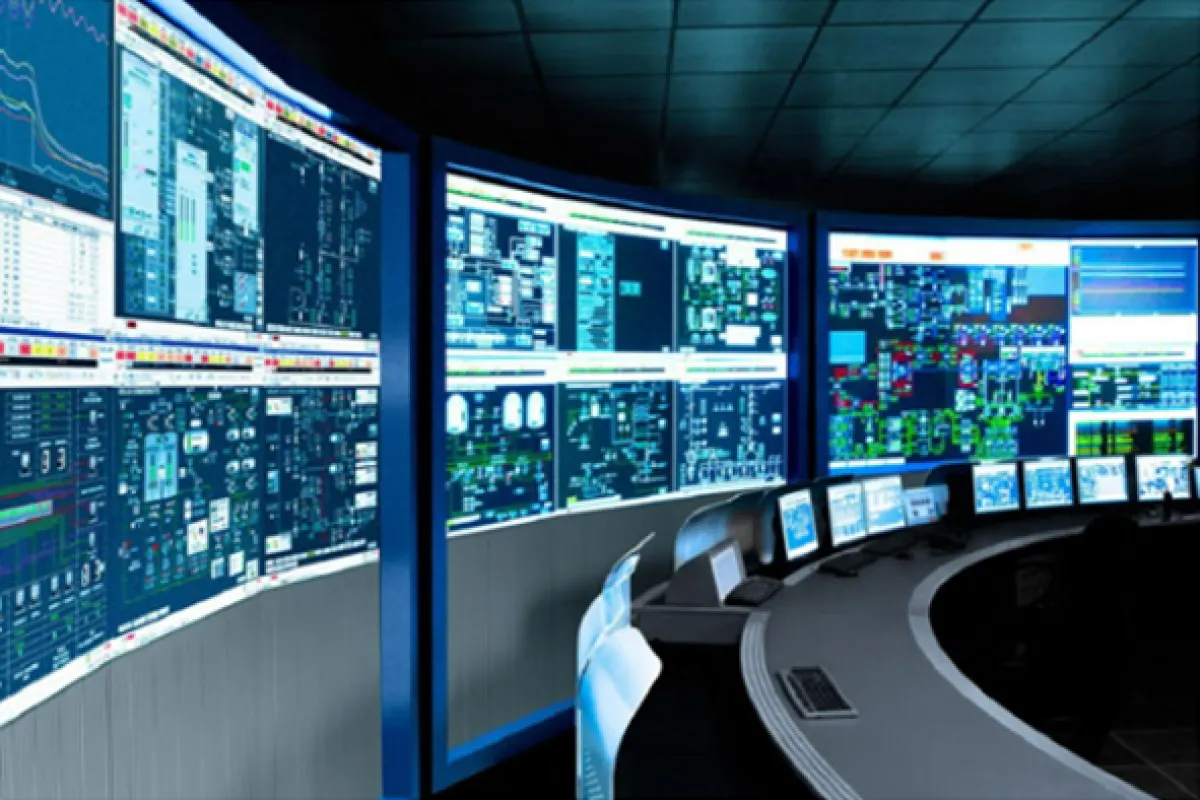

Control and Monitoring Systems
Function
Oversee and control plant processes.
Examples
⮞ SCADA Systems: Monitor and control industrial processes by collecting real-time data from remote locations. ⮞ Emergency Shutdown (ESD): Safeguard plant operations by automatically shutting down systems in emergency situations to prevent hazards. ⮞ Fire and Gas Detection Systems: Detect and alert operators to the presence of fire or hazardous gases, enabling quick response and mitigation.
Relays and Controllers
Function
Control processes and devices based on set conditions.
Examples
⮞Time Delay Relays: Control operations by introducing a delay before activating or deactivating a system based on a set time. ⮞ Safety Relays: Ensure safe operation by monitoring and controlling safety-critical functions in industrial systems. ⮞ Temperature Controllers: Regulate temperature within a process by adjusting heating or cooling devices according to preset limits.
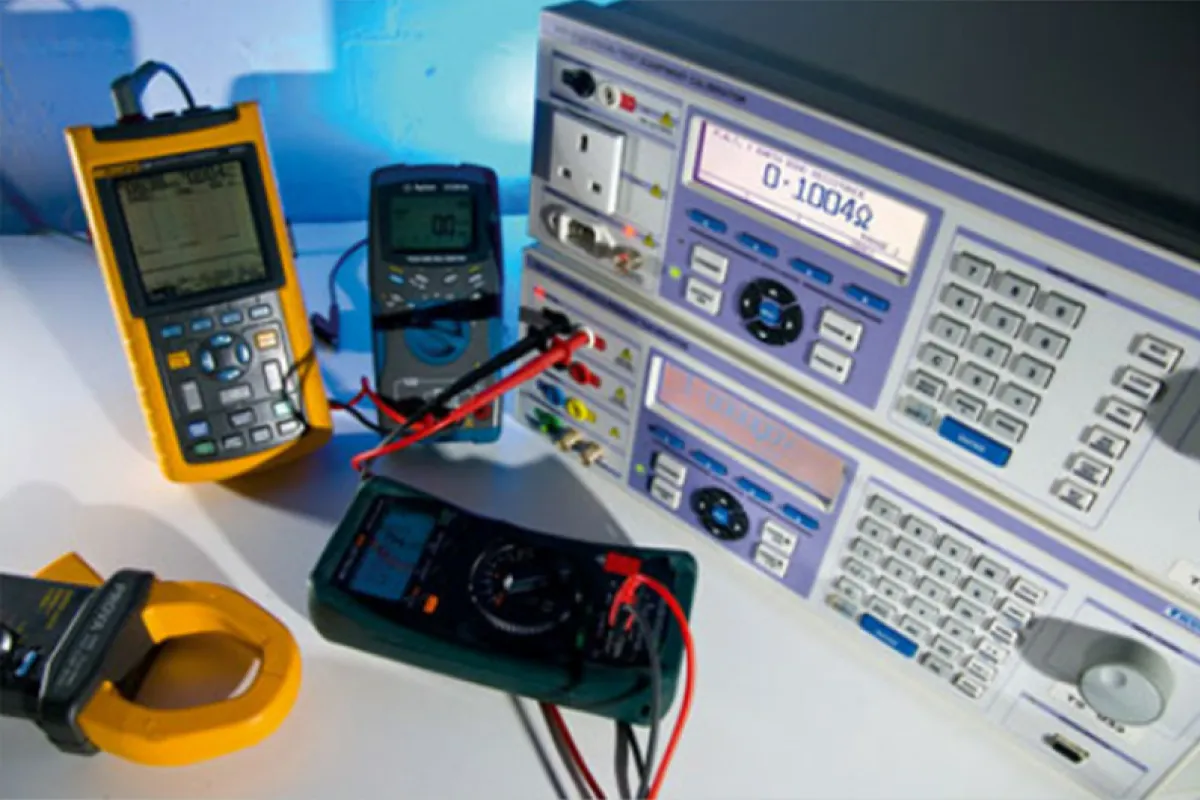

Calibration and Testing Equipment
Function
Ensure instrument accuracy.
Examples
⮞ Pressure Calibrators: Verify and adjust pressure measurement devices to ensure accurate readings. ⮞ Loop Calibrators: Calibrate and test instrumentation loops to maintain precise control and measurement. ⮞ Temperature Baths: Provide stable, controlled environments to calibrate temperature sensors and ensure accurate temperature readings.
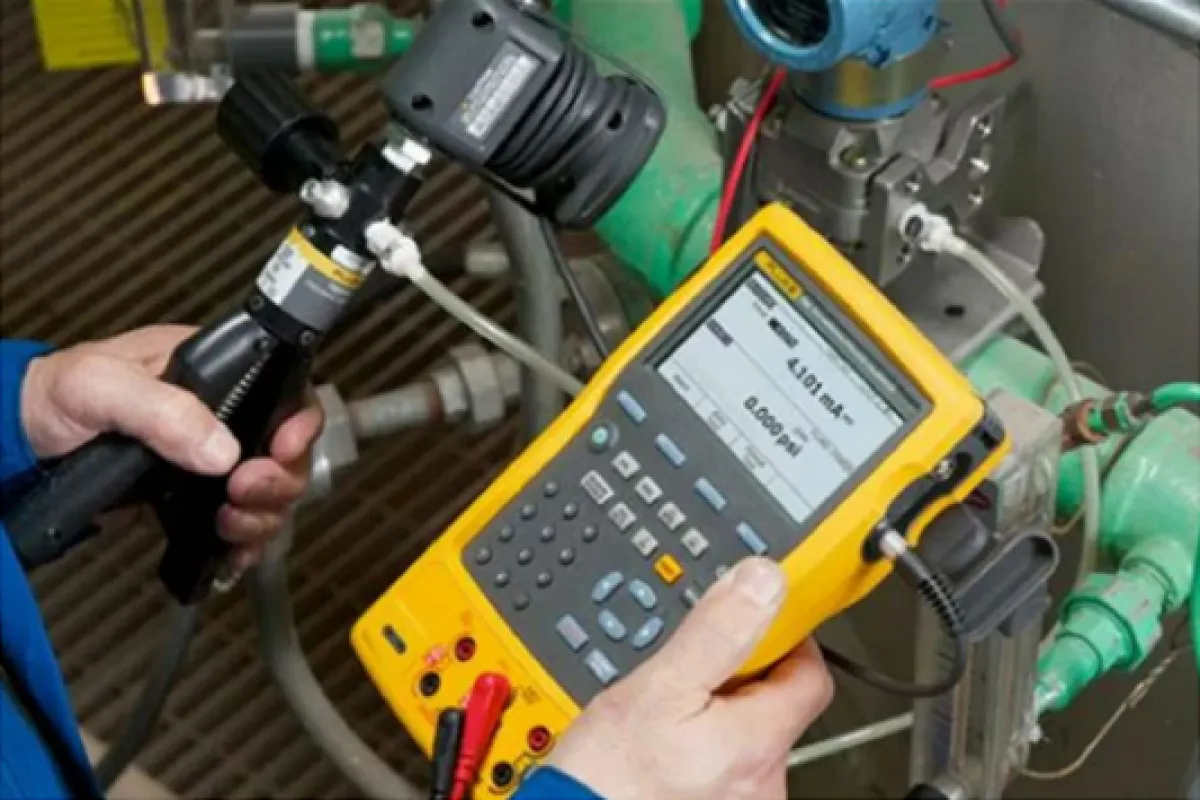

Field Instruments
Function
Monitor conditions in remote or hazardous areas.
Examples
⮞ Vibration Sensors: Detect vibrations and monitor machinery conditions to prevent damage in remote or hazardous environments. ⮞ Humidity Sensors: Measure moisture levels in the air to ensure optimal conditions in sensitive or hazardous areas. ⮞ Gas Detectors: Monitor for the presence of hazardous gases, providing early warning in unsafe or remote locations.

Signal Conditioners and Isolators
Function
Convert or isolate signals to ensure compatibility with control systems.
Examples
⮞ 4-20 mA to 0-10 V Converters: Convert current signals to voltage signals for compatibility with different control systems. ⮞ Isolated Signal Amplifiers: Amplify and isolate signals to prevent interference and ensure accurate transmission to control systems.
