Generators
- Home
- Generators
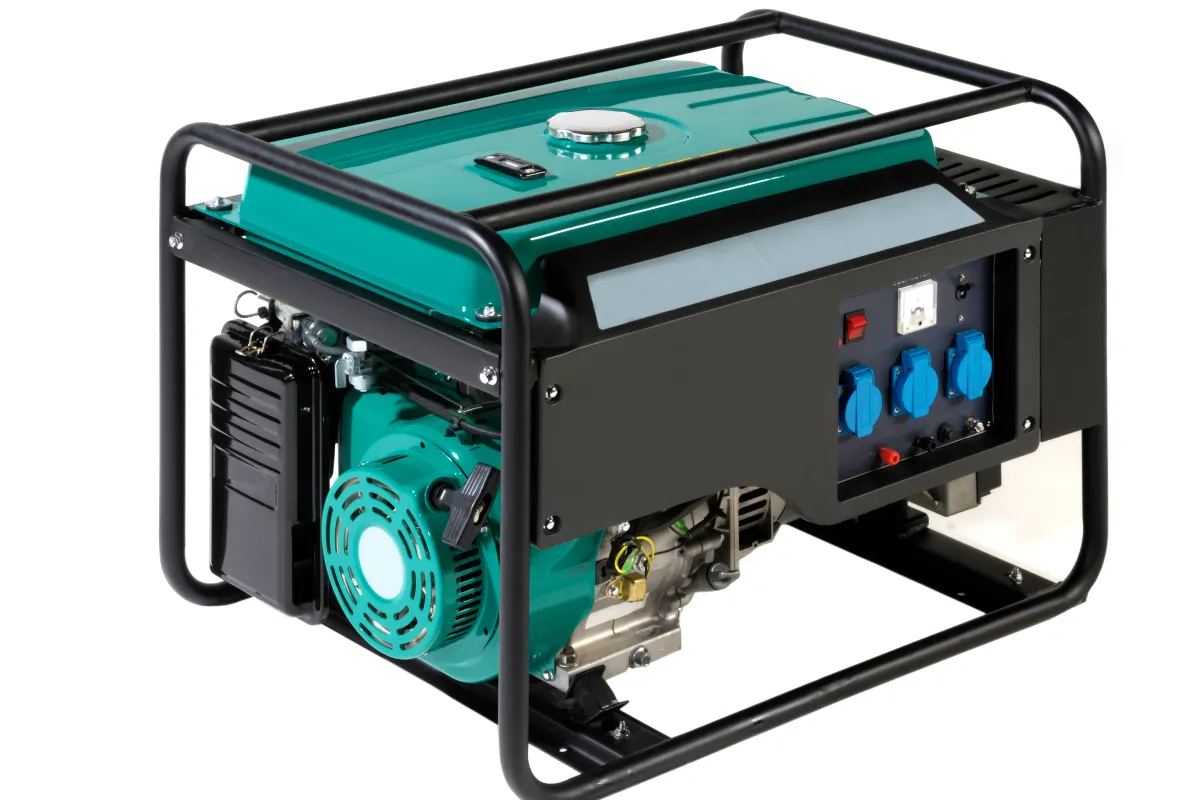

Portable Generators
Overview
Compact and lightweight, these generators are designed for easy transport and quick deployment.
Fuel Options
Typically powered by Diesel and petrol
Common Uses
Ideal for outdoor adventures, camping trips, and as an emergency power source for homes.
Key Components
⮞ Multiple power outlets to plug in devices. ⮞ Power output ranges from 1,000 to 10,000 watts.

Inverter Generators
Overview
These advanced portable generators produce clean and stable power.
Fuel Options
Generally powered by Diesel and petrol.
Common Uses
Perfect for powering delicate electronics, such as laptops and smartphones, ensuring steady voltage.
Key Components
⮞ Lightweight design and quieter operation. ⮞ Capability to connect multiple units for increased power.
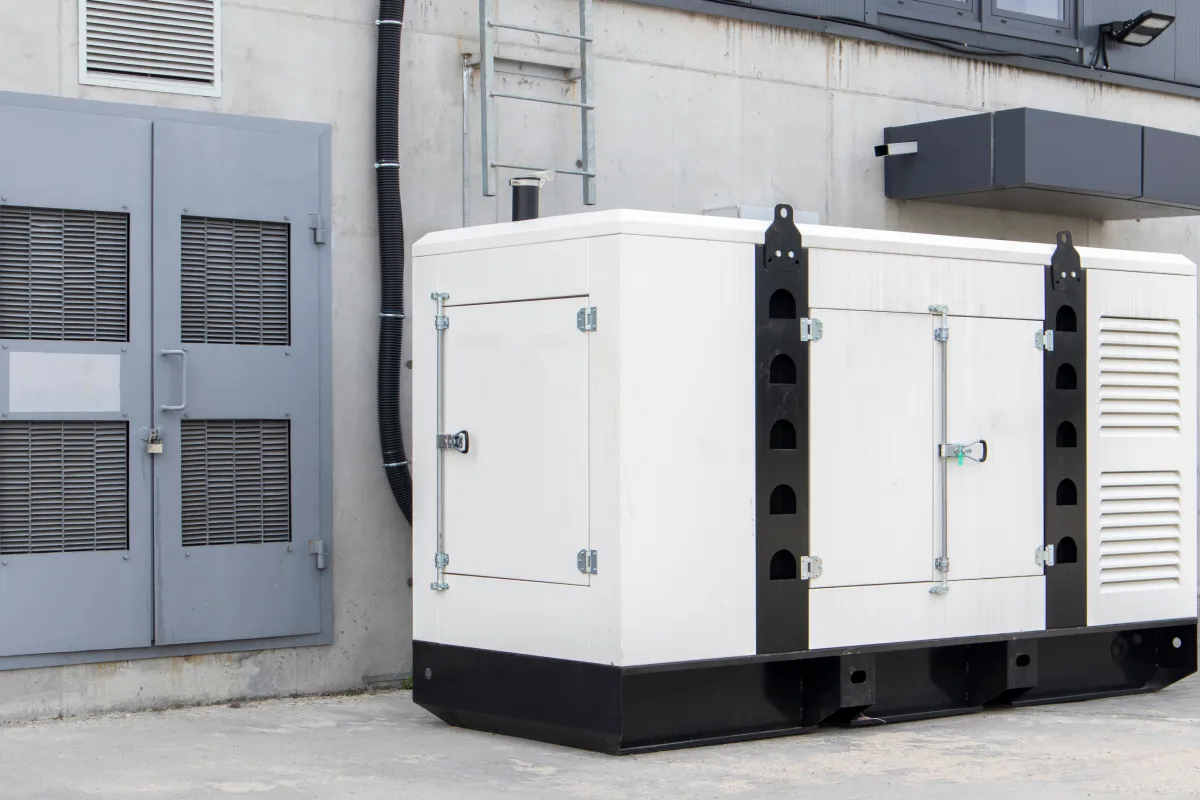

Diesel Generators
Overview
We offer wide range brands ( Perkins, FG Wilson, CAT , Cummins, Volvo Penta, Doosan, and more wide range of manufactures), starting sizes from 10kVA / 9 kW up to 2475Kva / 1080 kW.
Fuel Options
Commonly fueled by Diesel.
Common Uses
Widely used in homes, businesses, and critical facilities requiring uninterrupted power.
Key Components
⮞ Features an automatic transfer switch (ATS) for smooth power transition. ⮞ Offers a large power output, typically over 20,000 watts.
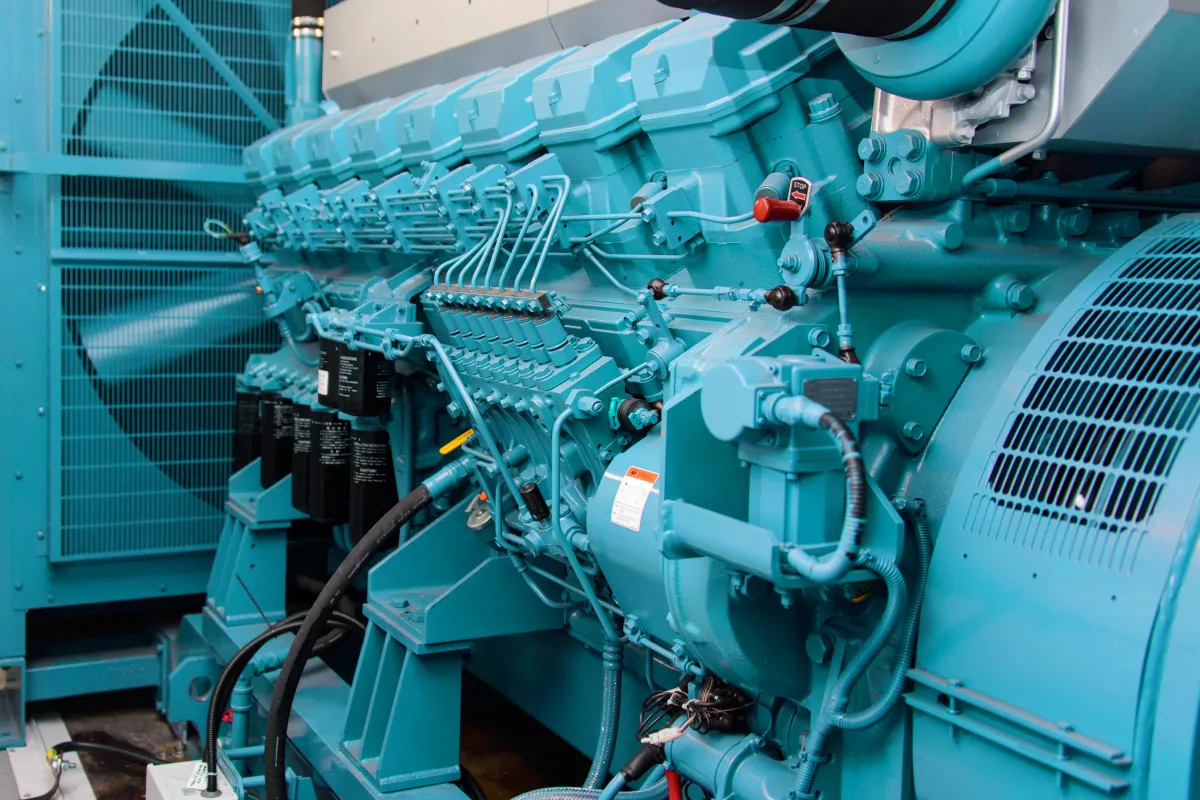
Industrial Generators
Overview
Heavy-duty generators built for substantial power demands.
Fuel Options
Can run on diesel, natural gas, or biofuels.
Common Uses
Utilized in construction sites, factories, and during emergencies for reliable, large-scale power.
Key Features
⮞ High-output power capabilities (up to several megawatts). ⮞ Durable and designed for extreme environments.
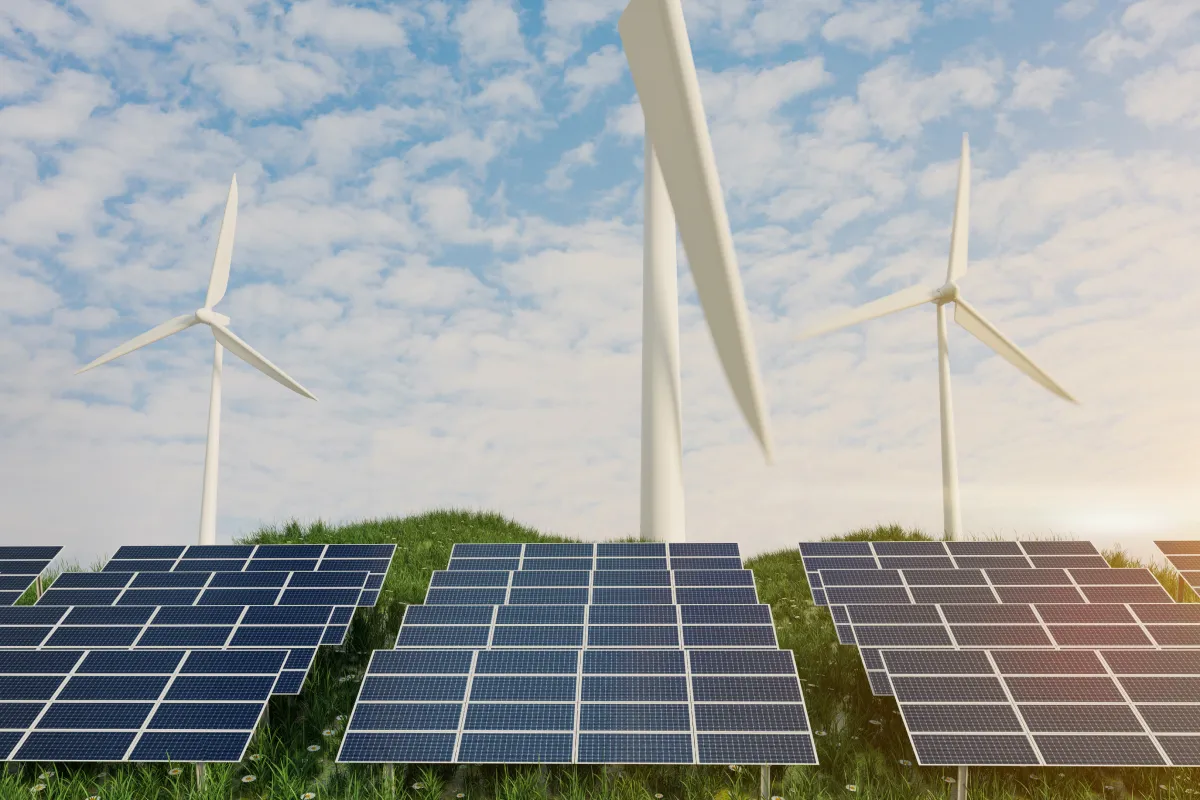

Renewable Energy Generators
Overview
Generators that utilize renewable energy sources to produce power.
Types
⮞ Wind Generators: Harness wind energy to generate electricity. ⮞ Solar Generators: Use solar panels to capture sunlight and convert it into power.
Common Uses
Great for off-grid living, remote areas, and reducing environmental impact.
Key Components of Generators
⮞Engine: Converts fuel into mechanical energy to drive the generator. ⮞ Alternator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical power. ⮞ Fuel System: Includes the fuel tank, pump, and lines to supply fuel to the engine. ⮞ Cooling System: Ensures the generator stays within safe operating temperatures. ⮞ Exhaust System: Expels exhaust gases from the engine and reduces noise levels. ⮞ Control Panel: Provides control and monitoring, allowing the operator to start or stop the generator. ⮞ Battery: Powers the starter motor and control systems. ⮞ Voltage Regulator: Maintains a stable voltage output to prevent fluctuations.
Applications of Generators
⮞ Residential Use: Provide reliable backup power during outages, keeping essential household systems running. ⮞ Commercial Use: Maintain business operations and ensure continuity during power interruptions. ⮞ Construction Sites: Supply power to tools and equipment at locations lacking access to the electrical grid. ⮞ Event Power: Provide electricity for outdoor events, festivals, and concerts. ⮞ Emergency Services: Vital for hospitals, disaster response teams, and other emergency facilities needing uninterrupted power.
